
What is Multi-factor Authentication?
Multifactor authentication (MFA) is a security mechanism that requires users to provide two or more forms of identification before granting access to a system or application. MFA is a more secure authentication method than traditional username and password because it adds an extra layer of security to verify the identity of the user.
MFA typically involves three types of factors:
- Something you know – Password
- Something you have - Email OTP/SMS OTP/Challenge Questions/Yubikey
- Something you are - Biometrics like a fingerprint or face scan.
QuickLaunch MFA Capabilities
Risk-based Authentication
Varity of authentication factors
MFA for mobile app
Adaptive MFA Policies
Role Based Access Control
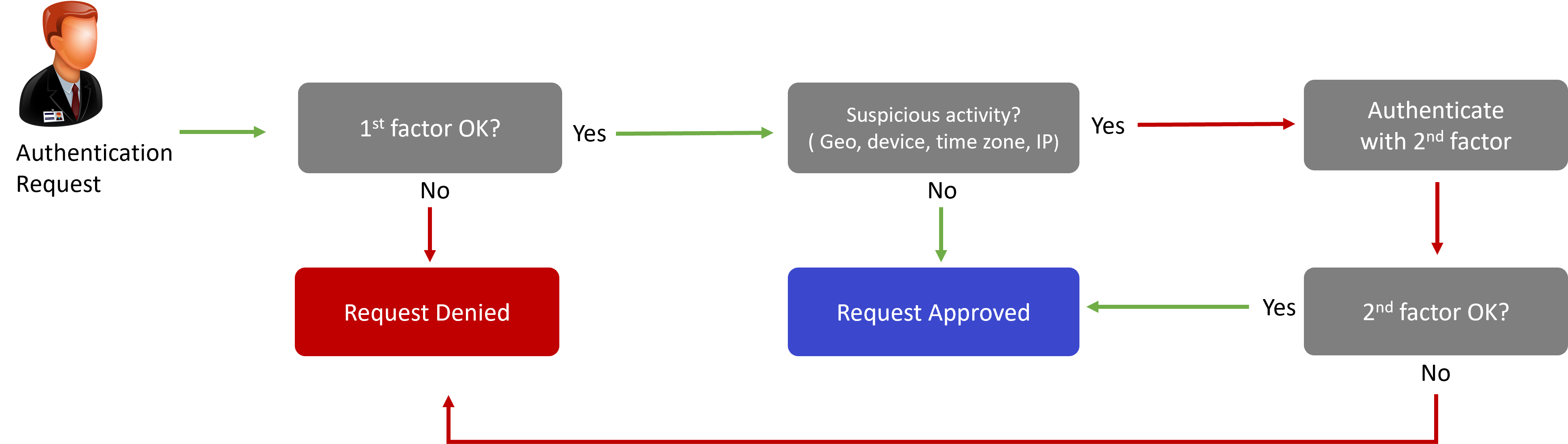
How risk based MFA works
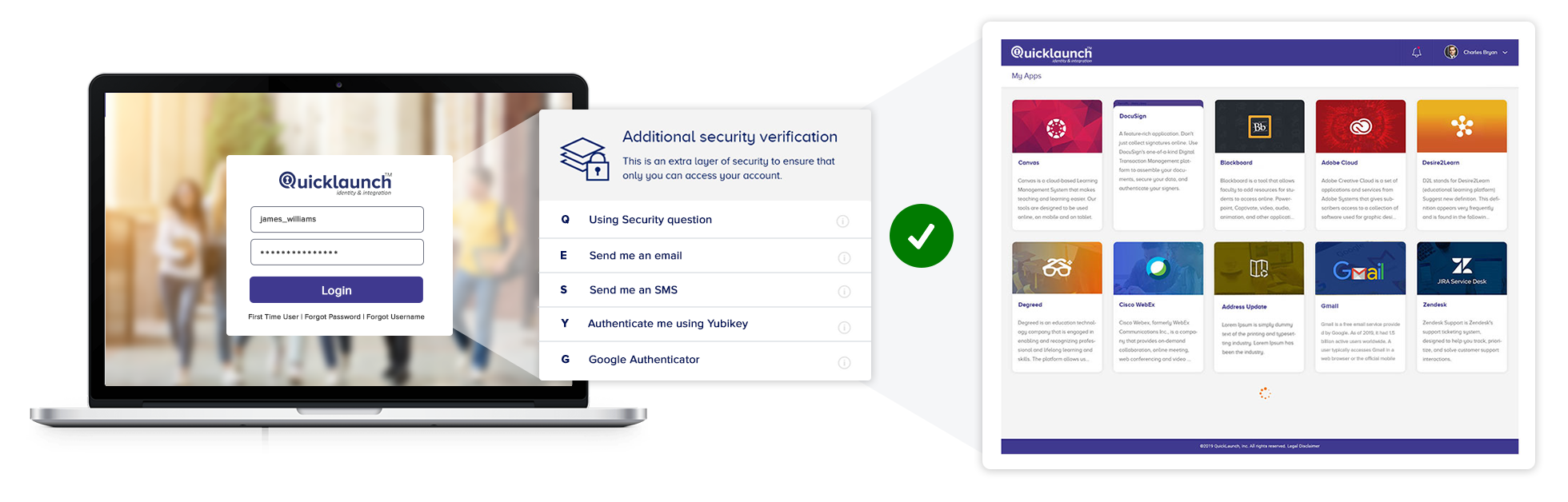
Enhance user experience with Adaptive MFA
Adaptive MFA is a game-changer in user authentication by elevating user experience by intelligently assessing the risk associated with each user interaction. By analyzing and recognizing normal user patterns, Adaptive MFA requests less information, allowing users to continue their work uninterrupted. Only when a potential security risk is detected will Adaptive MFA require additional validation from the user, providing a seamless and secure authentication experience.
App-level MFA
Step-up MFA is an additional security measure that enables limited access to an organization's most sensitive resources, thus adding one more layer of security to protect against unauthorized access and potential threats, giving you peace of mind that your organization's data and assets are secure.
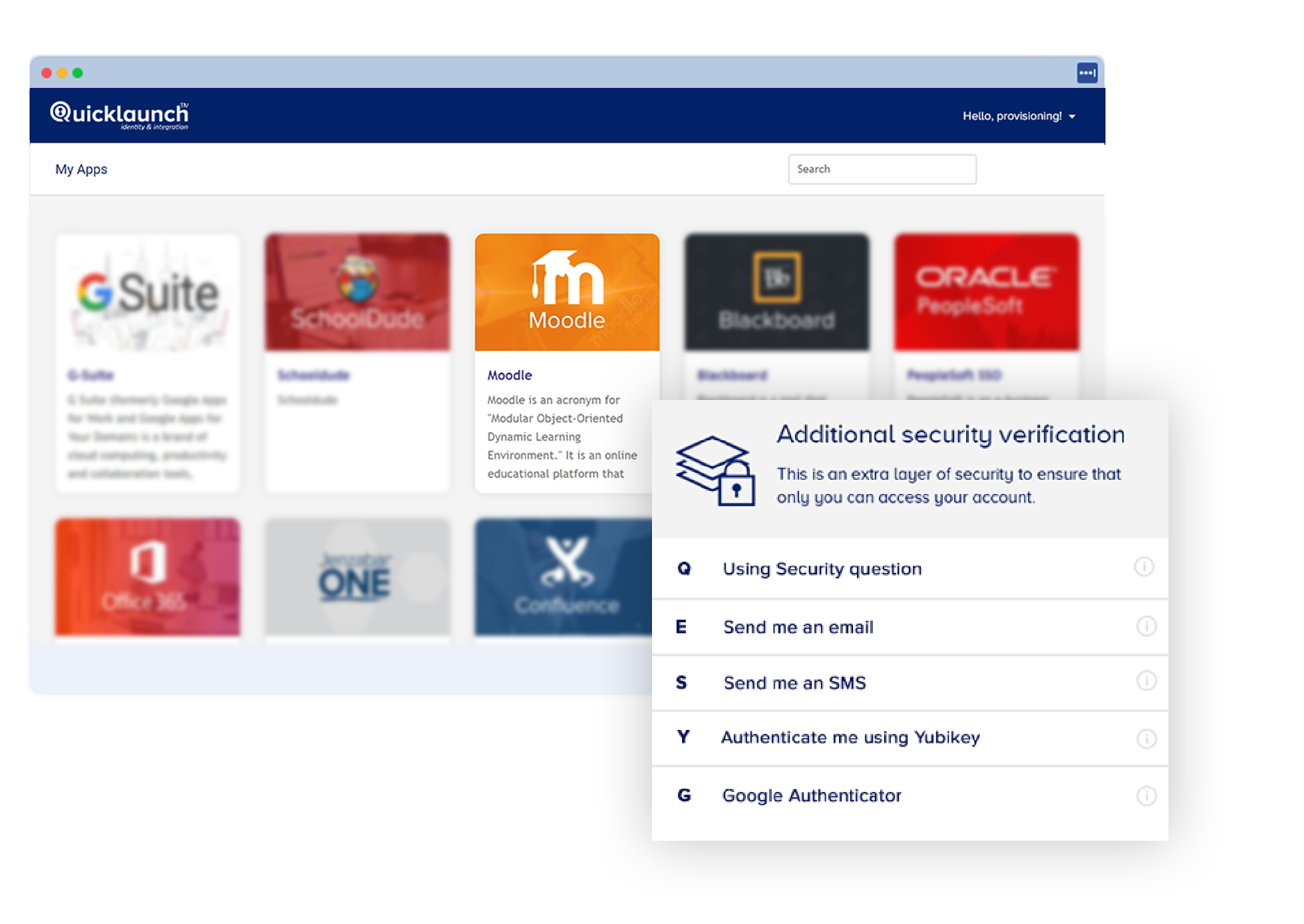
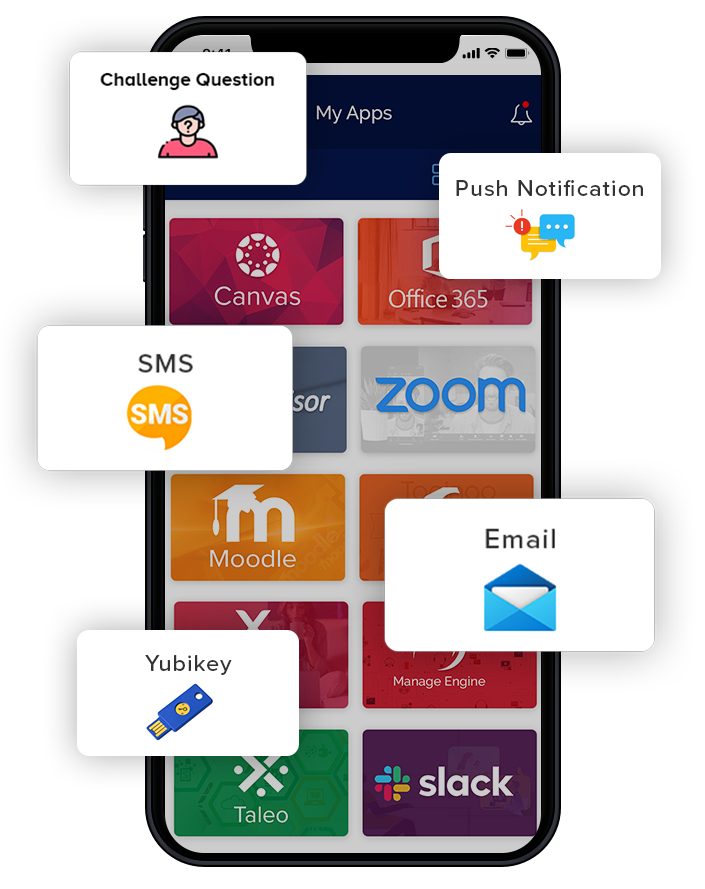
Multiple Authentication Factors
With support for various authentication factors, QuickLaunch provides both businesses and users with the flexibility to choose the authentication method that suits their needs best.
Types of Authentication factors:
- Security Questions
- Email OTP
- Phone OTP
- Google Authenticator
- Yubikey
- Mobile Push
- Microsoft Authenticator
- Face ID/Touch ID
